
Call 0330 880 3600 Calls may be monitored or recorded. Opening Times.
- TRAVEL INSURANCE
- COVID-19 ENHANCED COVER
- More Options
- Help & Advice
- Existing Customers

Call 0330 880 3600 Calls may be monitored or recorded. Opening Times.
Need help?
UK Customer Services0330 880 3600
Open Mon - Fri 9am - 5pm, Sat 8.30am - 4pm, Closed Sunday..
(Calls may be monitored or recorded)
Contact details can be found in your policy documentation
Available 24 hours a day, every day
Other Guides
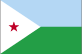
Region: Africa
Full Name: Republic of Djibouti
Capital City: Djibouti
Language Spoken: French (official), Arabic (official), Somali, Afar
Get travel insurance to Djibouti from Direct Travel Insurance. We offer low cost and high quality travel insurance to Djibouti and most of the world.

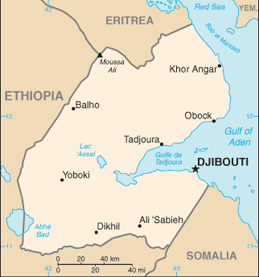
11 30 N, 43 00 E
lowest point: Lac Assal -155 m highest point: Moussa Ali 2,028 m
total: 516 km border countries: Eritrea 109 km, Ethiopia 349 km, Somalia 58 km
earthquakes; droughts; occasional cyclonic disturbances from the Indian Ocean bring heavy rains and flash floods
geothermal areas, gold, clay, granite, limestone, marble, salt, diatomite, gypsum, pumice, petroleum
arable land: 0.04% permanent crops: 0% other: 99.96% (2005)
inadequate supplies of potable water; limited arable land; desertification; endangered species
Extremely hot and particulary arid between June and August when the dusty Khamsin blows from the desert. Between October and April it is slightly cooler with occasional light rain; however, there is generally less than 150mm of rainfall annually.
time difference: UTC+3
486,530 (July 2006 est.)
0-14 years: 43.3% (male 105,760/female 105,068) 15-64 years: 53.3% (male 135,119/female 124,367) 65 years and over: 3.3% (male 8,183/female 8,033) (2006 est.)
total: 18.2 years male: 18.7 years female: 17.7 years (2006 est.)
2.02% (2006 est.)
39.53 births/1,000 population (2006 est.)
19.31 deaths/1,000 population (2006 est.)
0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2006 est.)
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female under 15 years: 1.01 male(s)/female 15-64 years: 1.09 male(s)/female 65 years and over: 1.02 male(s)/female total population: 1.05 male(s)/female (2006 est.)
total population: 43.17 years male: 41.86 years female: 44.52 years (2006 est.)
5.31 children born/woman (2006 est.)
Business meetings are formal and suits should be worn. French and Arabic are the main languages used in business. As there are few reliable interpreter services, knowledge of either of these languages is essential. Business entertainment will often take place in hotels or restaurants. Office hours are 0620-1300 Saturday to Thursday.
Petty crime occurs occasionally in the capital and elsewhere in the country, but violent crimes in urban areas are rare. Travel outside of urban areas at night should be avoided. Banditry and rebel activity is common near border areas, and these should be avoided.
Hotels in Djibouti tend to be expensive and the few cheap hotels are often rundown and lack most amenities. The major hotels are the Sheraton, the Hotel Plein Ciel, the Menelik and the R?sidence de l'Europe. Outside Djibouti, accommodation is limited, although attention is being given to upgrading and adding to the accommodation available in outlying areas.
Telephone IDD available. The country code is 253 and the outgoing international code is 00. There are currently no Fax facilities for the public. Telexes and telegrams can be sent from the main post office from 0700-2000. Telegram services are also available at the Telegraph office. Letters and parcels to Western Europe can take about a week by airmail or up to three weeks by surface mail.
is 220 volts AC, 50Hz. Electricity 220 volts AC, 50Hz.
C,E
Restaurants serve Arab, Chinese, French and Vietnamese local specialties.
National specialties:
? Lentils, fried meat and unleavened bread are all popular.
? Fish from the Red Sea. National drinks:
? Drinking is not a social activity and alcohol is not widely available.
Tipping:
A 10 per cent service charge is usually added to bills. Tipping is rare and never requested. Not usual for taxi drivers. A tariff is normally set but visitors will be charged at a higher rate.
Passport valid for six months beyond date of departure required by all.
Required by all except transit passengers not disembarking and continuing their journey by the same aircraft or ship.
Entry (visa de s?jour); Tourist (visa de tourisme); Business (visa d'affaires); Transit (visa de transit). All visas cost US$59
From one day to three months. An extension may be granted in Djibouti on request to the Headquarters of the Police Nationale.
The Embassy in Paris (see Passport/Visa Information). 10-day transit visas can be issued at the point of entry to visitors holding confirmed return air tickets. A fee will be charged. This facility is only available to nationals from countries where Djibouti has no diplomatic representation. Contact the Embassy in Paris for further information.
(a) Valid passport. (b) Two application forms completed in French. (c) Two passport-size photos. (d) Fee of ?50 plus ?5 to cover postage within France or ?6 to cover postage from abroad; the amount should be sent in the form of a postal or money order, not a cheque. (e) Return or onward ticket. Business: (a)-(e) and, (f) Letter from the employer or a letter of invitation from the company in Djibouti.
Three working days.
No Test Required
$US20 is levied on all passenge
26 rue Emile Menier, 75116 Paris, France
Tel: (1) 4727 4922.
Opening hours: Mon-Fri 0900-1600.
1156 15th Street, Suite 515, NW, Washington DC 20005, USA
Tel: (202) 331 0270.
Djibouti shares with the rest of the region a high threat from terrorism. Travelers are at risk from terrorist attacks in areas frequented by Westerners.
Travelers should be aware of the risk of banditry if traveling outside the capital city.
This advice is based on information provided by the Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office in the UK. It is correct at time of publishing. As the situation can change rapidly, visitors are advised to contact the following organizations for the latest travel advice:
Tel: (0845) 850 2829.
Website: www.gov.uk/foreign-travel-advice
Djibouti Franc (Djf) = 100 centimes. Notes are in denominations of Djf10,000, 5000, 2000, 1000 and 500. Coins are in denominations of Djf500, 100, 50, 20 and 10.
There are no restrictions on the import or export of either foreign or local currency. Currency must be declared on arrival.
Sat-Thurs 0715-1145.
Currency can be exchanged at major banks and hotels, or at authorized bureaux de change in the capital. The bureaux de change are open all day, while the banks have limited opening hours.
These are only accepted by airlines and some of the larger hotels.
To avoid additional exchange rate charges, travellers are advised to take travellers cheques in US Dollars or Euros. Euro and Sterling cheques are not accepted unless marked as 'External Account' or 'Pour Compte Etranger'. The majority of banks are in the place du 27 juin area.
Avoid dental care in Djibouti
Limited supplies of some medications are available from a hand full of European owned pharmacists in Djibouti
Blood supplies should be considered as unsafe throughout Djibouti, with the exception of blood supplied by the French Military Hospital
Medical facilities are limited and medicines are often unavailable.
Recent medical and dental exams should ensure that the traveler is in good health. Carry appropriate health and accident insurance documents and copies of any important medical records. Bring an adequate supply of all prescription and other medications as well as any necessary personal hygiene items, including a spare pair of eyeglasses or contact lenses if necessary. Drink only bottled beverages (including water) or beverages made with boiled water. Do not use ice cubes or eat raw seafood, rare meat or dairy products. Eat well-cooked foods while they are still hot and fruits that can be peeled without contamination. Avoid roadside stands and street vendors. Swim only in well-maintained, chlorinated pools or ocean water known to be free from pollution; avoid freshwater lakes, streams and rivers. Wear clothing which reduces exposed skin and apply repellents containing DEET to remaining areas. Sleep in well-screened accommodations. Carry anti-diarrheal medication. Reduce problems related to sun exposure by using sunglasses, wide-brimmed hats, sunscreen lotions and lip protection.
AIDS occurs. Blood supply may not be adequately screened and/or single-use, disposable needles and syringes may be unavailable. When possible, travelers should defer medical treatment until reaching a facility where safety can be assured.
Cholera: Although limited in effectiveness, vaccination may be appropriate for persons living and/or working in less than sanitary conditions for more than 3 months where medical facilities are unavailable. Vaccination may also be appropriate for travelers with impaired gastric defenses who are planning an extended visit or being exposed to unsanitary conditions. Vaccination is not advised for pregnant women, infants younger than 6 months old, or persons with a history of severe reaction to the vaccine. Hepatitis A: Consider active immunization with hepatitis A vaccine or passive immunization with immune globulin (IG) for all susceptible travelers. Especially consider choosing active immunization for persons planning to reside for a long period or for persons who take frequent short-term trips to risk areas. The importance of protection against hepatitis A increases as length of stay increases. It is particularly important for persons who will be living in or visiting rural areas, eating or drinking in settings of poor or uncertain sanitation, or who will have close contact with local persons (especially young children) in settings with poor sanitary conditions. Hepatitis B: Vaccination is advised for health care workers, persons anticipating direct contact with blood from or sexual contact with inhabitants, and persons planning extended stays of 6 months or greater (especially those who anticipate using local health care facilities, staying in rural areas, or having intimate contact with the local population). Meningitis: Meningococcal vaccine is recommended for travelers, particularly during the December-June dry season when epidemics are most likely to occur. Importance of vaccination increases with length of stay and/or exposure to crowded conditions. Pregnancy is a relative contraindication to vaccination. Protection may be less effective for infants and children aged 3-23 months than it is for persons aged 2 years and older. Polio: A one-time booster dose is recommended for travelers who have previously completed a standard course of polio immunization. Refer to CDC guidelines for vaccinating unimmunized or incompletely immunized persons. Pregnancy is a relative contraindication to vaccination; however, if protection is needed, either IPV or OPV may be used, depending on preference and time available. Typhoid: Vaccination should be considered for persons staying longer than 3 weeks, adventurous eaters, and those who will venture off the usual tourist routes into small cities, villages and rural areas. Importance of vaccination increases as access to reasonable medical care becomes limited. Contraindications depend on vaccine type. Note: All routine vaccines (such as DTP or Td, Hib, MMR, polio, varicella, influenza and pneumococcal) should be kept up-to-date as a matter of good health practice unrelated to travel.
Insect-borne diseases: are major causes of illness. Many diseases are endemic, with only scattered cases being reported and, from time to time, more extensive outbreaks. Dengue fever - occurs Filariasis - prevalent Leishmaniasis - occurs (both cutaneous and visceral types may be found, particularly in the drier areas) Malaria - prevalent Relapsing fever - occurs Typhus - occurs (louse-, flea-, and tick-borne typhus occur) Food-borne and water-borne illness: highly endemic. The dysenteries and diarrheal diseases (including cholera), giardiasis, the typhoid fevers and viral hepatitis are widespread. Echinococcosis (hydatid disease) is widespread in animal-breeding areas. Guinea-worm infection - occurs Helminthic (parasitic worm) infections - prevalent Schistosomiasis - common Other hazards: Diseases such as measles and diphtheria are commonly reported. Polio is still considered a possible risk, although cases have rarely been reported in recent years. Influenza risk extends throughout the year. Meningococcal meningitis - occurs (risk is highest during the December-June dry season, when epidemics are most likely) Rabies - reportedly rabies-free (although this status is considered provisional) Trachoma - prevalent
Yellow fever: A yellow fever vaccination certificate is required from travelers over 1 year of age coming from infected areas. (Contrary to its published requirements, the U.S. Embassy reports that a yellow fever vaccination certificate is required for all visa applicants; however, this policy may not be consistently enforced.)
No recent disease outbreaks
| Name | Address |
|---|---|
| Centre Hospitalier des Arm?es Bouffard | Between Avenue Charles de Gaulle & Avenue de la Siesta By railway tracks By railway tracks |
The main newspaper, La Nation, is owned by the government, as is Radiodiffusion-T?l?vision de Djibouti (RTD), which operates the national radio and TV. There are no private broadcasters. All electronic media is closely controlled by the government. Private newspapers and other publications are generally allowed to circulate freely, but journalists exercise self-censorship. The official media does not criticize the government. US-sponsored Arabic-language Radio Sawa broadcasts programs to East Africa and Arabia from a transmitter in Djibouti.
Press: Djibouti has no daily papers. A weekly newspaper, La Nation, is government-owned and published in French. There is at least one Arabic newspaper. Other weekly newspapers published in French include Le Renouveau, La R?publique (both owned by the opposition party), Le Progr?s, and Le Temps.
TV: Djibouti T?l?vision is Government-owned.
Radio: Radio Djibouti is Government-owned and broadcast in Afar, Arabic and Somali.